rcore-arceos-hypervisor虚拟化抖动入坑
0. tmp
1 | |
https://github.com/MROS/hypervisor-blog
1. 基础设施
为了方便调试,建议在hypervisormain中添加断言,当boot_hart不为0号hart时直接退出。跑通后再支持随机hart的启动。
2. arceos SMP启动过程
好东西-->https://mermaid.live/
从核在走完启动流程后会wfi,然而不能对已经wfi的hart进行
sbi::hart_start,会报告SBI_ERR_ALREADY_AVAILABLE已经启动。那么如何让从核到指定位置继续运行?答案是别管,直接侵入arceos部分,直接在wfi-loop前添加函数,让其跳转到新的入口,不进入wfi
3. hypervisor虚拟化
a. cpu虚拟化
arceos启动完成后,跳入hypervisor的main(hartid)。hypervisor依次做以下工作:
1 | |
首先为物理cpu创建结构。它会根据cpu数量,获取一块固定大小的内存,并将其按照cpu数量等分,形成类似于一个数组的结构。分配完成后,“数组”的首地址被存入PER_CPU_BASE中。
“数组”下标为cpi_id的元素存放着对应cpu的信息。这些信息包括cpu_id,栈地址和此物理cpu绑定的vcpu队列等(marker: core::marker::PhantomData<H>不懂是干啥的)。
这个结构配合tp寄存器,可以在执行流中找到当前的物理cpu信息。在每个物理cpu上执行一次setup_this_cpu,就可以让每个cpu的tp保存各自的PerCpu结构位置。那么在执行流的任意位置使用this_cpu(),就能通过tp获得当前物理cpu的PerCpu结构,进而得到当前运行在几号物理cpu上/此物理cpu绑定哪些vcpu等信息。
然后,hypervisor解析设备树文件,并据此设置两阶段内存转换页表。这部分内容放到内存虚拟化中详细说明。
1 | |
然后,根据PerCpu创建vcpu,它实际上是在PerCpu的绑定队列里添加vcpu_id,然后根据vcpu的id和入口地址,创建一个新vcpu结构。
1 | |
vcpu结构最主要的功能是保存V模式/非V模式的寄存器。进入/退出guest时,会对regs进行读取/保存。VCpu<H>::new(...)会设置一些虚拟化相关寄存器,然后设置a0/a1/sepc,构造一个上下文环境,使得在sret后可以回到entry执行;在hypervisor的main中,这个entry实际上就是linux的入口0x9020_0000(因为arceos的启动命令默认会把linux.bin放到这个位置,详情可在make
run时使用-nB参数打印所有命令查看)。而a0/a1需要保存启动hart_id和设备树文件地址,这是riscv
linux的规定,它需要接受这些信息才能启动。
riscv linux 启动文档: https://docs.kernel.org/translations/zh_CN/arch/riscv/boot.html
回到main中,创建vcpus,为vcpus添加vcpu,然后根据vcpus和页表创建vm。
1 | |
vcpus只是一个聚合多个vcpu的结构,为vm提供一层抽象。而vm在组合了vcpus和页表后,就具备了运行虚拟机的能力。
1 | |
至此,可以启动vm运行guest了。init_vcpu会从vcpus中获取对应id的vcpu,然后设置其regs中的hgatp为两阶段转换页表地址,并直接通过csrw hgatp写入当前物理cpu的hgatp。
应该如同其他csr一样,
hgatp在每个hart上都具备。
然后vm.run会调用vcpu的run(),实际上最后会来到_run_guest(regs)。_run_guest(regs)是一段汇编,它会保存hypervisor的寄存器到内存(即regs内),并替换为regs中guest的寄存器值,完成到guest的上下文切换,然后sret到之前构造好的linux入口环境中。
此处还会将stvec设置为_guest_exit,同样为一段汇编,就在_run_guest下方。这样做相当于劫“劫持了”arceos的中断向量:本来s
mode的trap会进入arceos指定的stvec地址,然而此处将其替换为_guest_exit地址,使得s
mode的trap不再交给arceos的中断处理程序,而是让hypercraft的部分处理中断。
_guest_exit类似于做_run_guest相反的操作,保存guest上下文,回到hypervisor中。设置stvec为_guest_exit,可以让linux在ecall时,跳转到_guest_exit,进而回到host即hypervisor中,而不进入arceos的中断处理程序。
当从_guest_exit退出guest后,会回到vcpu.run()中,根据scause分析原因并进一步退回vm.run(..)。vm.run(...)根据不同的原因,执行不同的操作,将结果写回vcpu的regs中,在下一轮_run_guest时,这些结果会被linux获知。
在linux
kernel眼中,自己就是执行了ecall,然后得到了结果而已。它并不清楚ecall召唤的原来是hypervisor,也不知道自己的寄存器值已经被换出去一轮了,就好像自己真的在物理cpu上运行一样。而hypervisor的任务就是模拟一个硬件环境,让guest不得而知,自己却能捕捉guest的行为。
stvec仍由hs mode控制,在当前场景下,hypervisor通过替换
stvec并设置hideleg/hedeleg来统领中断处理,替代了原先arceos中断处理的部分。而vstvec完全交由guest os进行处理,在V=1的情况下,guest对stvec的读写实际会被导向vstvec。guest os执行ecall后,会触发hs mode的trap;由于
stvec被替换为_guest_exit,因此会回到host部分,host再经由scause获知guest 触发了ecall
b. 内存虚拟化
两阶段地址翻译:GVA --> GPA --> HPA
其中guest os维护GVA --> GPA这部分转换,hypervisor需要维护GPA --> HPA这部分转换。
首先,arceos在页表初始化时会为虚拟化分配空间,总体为2GB:
1 | |
然后,hypervisor会从dtb读取地址布局,并建立GPA -->
HPA的等值映射,详见pub fn setup_gpm(dtb: usize) -> Result<GuestPageTable>
大致布局如下:
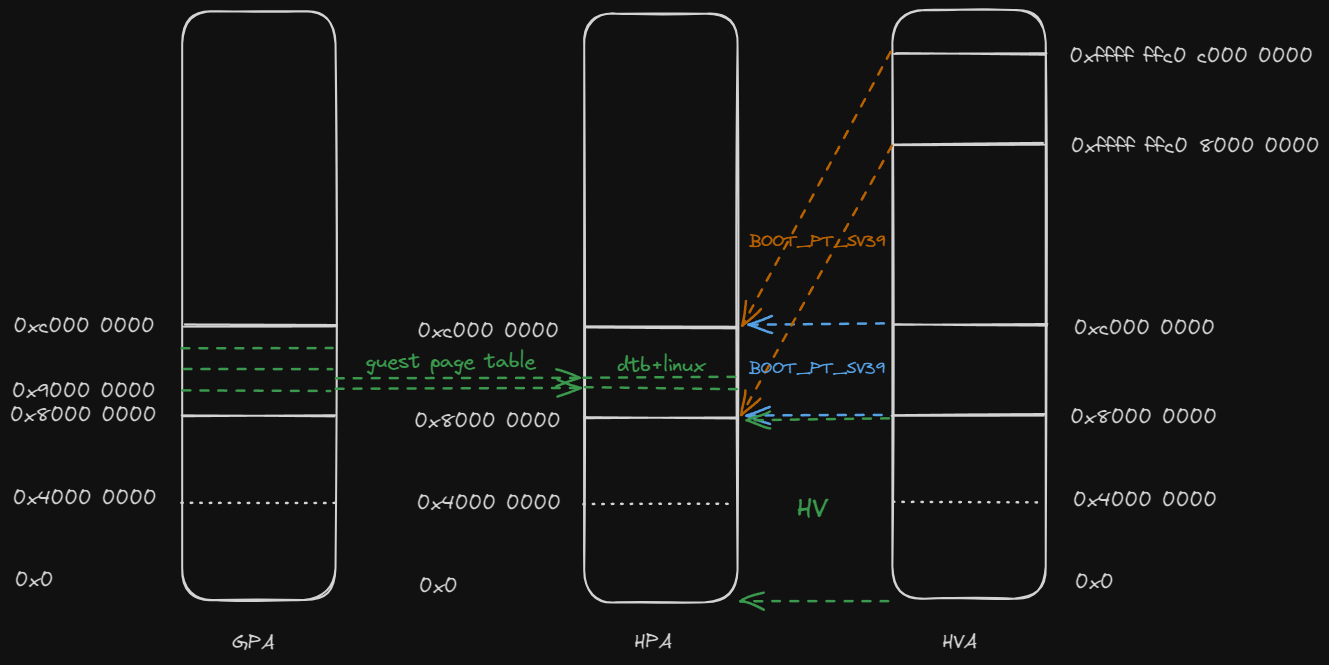
缺了mmio的一些映射,大体上应该差不多
c. 中断虚拟化
以guest os一次设定计时器的操作为例:
- arceos初始化时设置了虚拟化拓展环境,位于
crates/hypercraft/src/arch/riscv/mod.rs,其中设置了hideleg,使HS模式的所有中断都委托给了VS模式,也就是guest os所处的模式 - guest os调用
sbi::set_timer,设置定时器 - ecall触发vmexit,此行为被捕获,hypervisor得知guest
os调用了
sbi::set_timer - 于是hypervisor调用
sbi::set_timer,设置了定时器,并使能S模式时钟中断1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10HyperCallMsg::SetTimer(timer) => {
sbi_rt::set_timer(timer as u64);
// Clear guest timer interrupt
CSR.hvip.read_and_clear_bits(
traps::interrupt::VIRTUAL_SUPERVISOR_TIMER,
);
// Enable host timer interrupt
CSR.sie
.read_and_set_bits(traps::interrupt::SUPERVISOR_TIMER);
} - 一段时间后,定时器生效
- 由于之前设置了hideleg,所有中断都委托给了VS模式;于是guest os触发了时钟中断,并vmexit,此时guest os本身并不知情。
首先,中断/异常委托应该会产生委托目标那一级的中断/异常;例如在mideleg将时钟中断委托到s mode,那么当中断来临,pc应该会跑到stvec指示的地址,并且在scause写入原因为s mode时钟中断。那么当hideleg将时钟中断委托到vs mode时,实际上会在vs mode产生一个vs mode虚拟时钟中断?但会经过
vscause翻译让vs mode认为是触发了s mode时钟中断?如果这样的话,理应会跳转vstvec即guest os的中断处理程序,而不会跳转stvec回到host?所以我不太理解为什么hypervisor在vcpu.rs能通过scause为SupervisorTimer,来判断虚拟机获得了时钟中断。确实有问题,Xideleg并不意味着中断直接到对应的mode了,而是要通过Xip进行注入的。 https://danielmangum.com/posts/risc-v-bytes-timer-interrupts/#step-0-differentiating-machine-and-supervisor-timer-interrupts
- 时钟中断被捕获,hypervisor得知guest os遇到了时钟中断
- 于是hypervisor通过
hvip向guest os注入中断,并清除S模式中断使能1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9VmExitInfo::TimerInterruptEmulation => {
// debug!("timer irq emulation");
// Enable guest timer interrupt
CSR.hvip
.read_and_set_bits(traps::interrupt::VIRTUAL_SUPERVISOR_TIMER);
// Clear host timer interrupt
CSR.sie
.read_and_clear_bits(traps::interrupt::SUPERVISOR_TIMER);
} - guest os继续运行,获知发生时钟中断
以上达成的效果是:guest os设置定时器,并在一段时间后获知了时钟中断的发生。
由于替换了stvec,因此guest
os的异常/中断行为被hypervisor拦截/管控,hypervisor负责将其通知给guest
os,称为中断注入。
todo: 对吗?
这部分比我想的要复杂更多。一个关键困惑是,当时钟中断来临,系统还处在host运行时,不会进入arceos的irq_handler吗?
见后日谈
4. Linux SMP启动过程
smp多核启动(riscv架构) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
5. hypervisor多核
a. 多核dtb
首先要让guest linux感知到有多核硬件的存在,这部分由设备树文件表示。正常情况下,设备信息应该是由firmware告知操作系统的,而我们现在只需要虚构一个合理的多核硬件平台就行,让guest linux以为真的存在这些硬件。
/arceos/apps/hv/guest/linux下已经有了linux.dtb和对应的linux.dts了,对.dts进行修改,给予一个双核心,注意对原文件进行备份。
1 | |
使用dtc(Device Tree Compiler)将 DTS 文件编译为 DTB
文件。命令格式如下:
1 | |
b. sbi_call: hart_start
修改dtb后运行应该会报错:
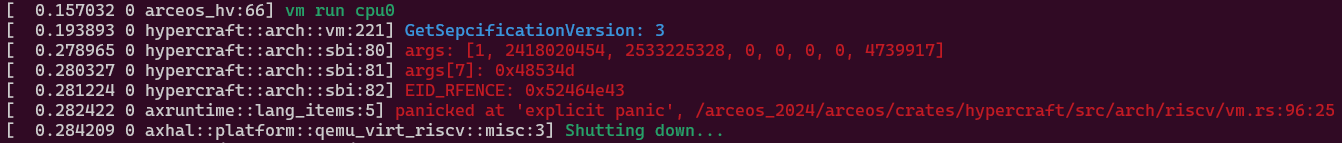
1 | |
位置在hypercraft::arch::sbi:80的80行,这意味着遇到了未知的sbi_call。
此时应该回到sbi手册,据手册所说:
1 | |
根据以上报错信息,得知EID = a7 = 0x48533d = 4739917,FID = a6 = 0,查找手册得知对应的内容为Chapter 9. Hart State Management Extension (EID #0x48534D "HSM")中的小节9.1. Function: HART start (FID #0)。
签名为: 1
2
3
4
5struct sbiret sbi_hart_start(
unsigned long hartid,
unsigned long start_addr,
unsigned long opaque
)
此函数要求目标hart以supervisor模式在start_addr地址开始运行,并且寄存器会被设置为以下格式(这都是从sbi手册上抄的):
| Register Name | Register Value |
|---|---|
| satp | 0 |
| sstatus.SIE | 0 |
| a0 | hartid |
| a1 | opaque parameter |
其余寄存器不做定义。
可以分析得出,guest
linux在知晓第二个核心存在后,就调用sbi_hart_start(1, 2418020454, 2533225328)来启动第二个核心,让其从指定地址开始运行。
hypervisor捕获了这一行为,但暂时还没有添加此sbi类型。因此我们需要补齐这部分功能,让hypervisor正确识别sbi_hart_start,并做相应处理。
补充这部分功能后,应该能正常进入guest linux了,不过此时多核肯定还没有完成,可以看到开机信息中显示启动cpu失败:
1 | |
毕竟我们还没有真的去运行sbi_hart_start中指定位置的代码。guest
linux发出了启动hart的请求,却没有收到响应,那么它自然会认为此核心异常,并报告失败。
因此,我们应该启动一个vcpu,遵照上面的状态,让其从指定地址开始运行,给guest linux提供“真的有核心在听我话”的错觉。
c. secondary运行
最终想要的效果是,当收到主核的sbi::hart_start后,根据参数设置寄存器初始状态,然后让第二个hart去运行vm.run(1)。
我们需要准备一个新的入口地址hv_secondary_main,让第二个hart跳转到此处,好进行下一部分设置。就目前的项目情况看,可以直接修改arceos的rust_main_secondary,添加hv_secondary_mainextern函数调用,让hart直接跳转进去。
在第二个hart进入hv_secondary_main后,需要将PerCpu结构设置到tp寄存器,并向vm添加新的vcpu,然后进行vm.init_cpu(1) & vm.run(1)。
这涉及到一些同步问题。首先,要向vm添加新的vcpu,必须存在vm。这要求主核创建vm以后,从核才调用vm.add_vcpu(...)。其次,主核需要等待所有从核都向vm添加vcpu后,才能开始运行vm.run(0),否则开始运行时vcpu数量是缺失的,可能会出问题。
最后,从核需要等待主核调用sbi::hart_start,获取目标地址等参数后,才能为vcpu设置对应寄存器,才能正式运行vm.run(...)。因此需要一个状态表示vcpu是否可以运行,并且让主核心来控制从核的这个状态。框架代码中包含了VmCpuStatus,可以修改后使用:
1 | |
vcpu在运行前需要检查这个状态,来决定是否可以运行,同时主核心应该在处理sbi::hart_start时,根据参数设置vcpu寄存器,完成后将vcpu状态设置为可运行。
总体流程差不多是下面这样。目的就是让guest os产生“自己直接运行在硬件上”的错觉。
d. sbi_call: send_ipi
下面继续运行的话,会出现新的未知sbi_call。
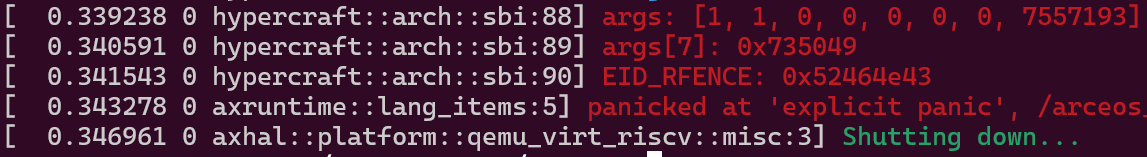
1 | |
这是guest linux的主从核同步过程,主核向从核发送ipi让其跳出wfi。详见linux smp启动过程。
TODO: linux smp
仿照hart_start,在hypervisor中进行处理,真正调用send_ipi即可。
根据sbi手册所述,发送核间中断会在目标hart触发一个supervisor software interrupts,这会表现为Unhandled trap: Interrupt(SupervisorSoft),需要我们补充相关信息,仿照vcpu.rs和vm.rs中异常处理的相关内容即可。
e. 中断注入
收到ipi的hart触发supervisor software interrupts后,会跳转中断向量,即在_run_guest中被修改为的_guest_exit,此时中断被hypervisor捕获,guest
os并不知情。
因此我们需要将软件中断注入guest中。
群里的蔡存哲老哥也提到了虚拟化中断这块内容,我正好也翻了一遍手册学到了点新东西,贴一手聊天记录摘要。
蔡存哲:Riscv 在 hs 模式往 hvip 注入定時器中斷之後,虛擬機會看到什麼?sip 被設置嗎?那 hip 有什麼作用?看了spec還是不太明白
我:虚拟机视角下应该只有vsip,根据手册中所述,当hideleg设置了时钟中断代理后,vsip.STIP等价于hip.VSTIP。而hip.VSTIP是只读的,它的值为(hvip.VSTIP || 导向VS mode的时钟中断信号)。因此,当hvip被设置后,会反应到hip中,等价于反应到vsip中。我的理解是hip是用来“综合中断信息”的,它表示虚拟机实际有没有中断,即有没有来自hvip的虚拟中断注入,和有没有实际的中断信号
蔡存哲:那當虛擬機去清除 vsip.STIP 時,hvip.VSTIP 是否會跟著被清除? 蔡存哲:反過來,hvip.VSTIP被hypervisor設置的同時,vsip.STIP是否跟著被設置,抑或是跳入VS mode時vsip.STIP才被跟著設置?Hypervisor感覺可以直接設置vsip.STIP 來注入中斷吧?不明白為何要多透過一個 hvip 來間接注入
我:对os来说,应该不会直接操作sip吧。因为手册提到sip是只读的,是由执行环境设置/清除的。“Bits sip.STIP and sie.STIE are the interrupt-pending and interrupt-enable bits for supervisor level timer interrupts. If implemented, STIP is read-only in sip, and is set and cleared by the execution environment.”
我:这个时机手册似乎没有提到,可能是硬件设置的。理论上只要满足vsip能够正确反应中断状态,什么时候被设置都行
我:这个我也不太懂,可能有个隔离的作用。 https://lists.riscv.org/g/tech-privileged/topic/question_on_the_new_hvip/74064351 有人问过类似的问题,这个回答没太看懂,好像是有关软件保存的问题
蔡存哲:它這個ececution environment 意思比較含糊 蔡存哲:https://github.com/riscv-non-isa/riscv-sbi-doc/blob/master/src%2Fext-time.adoc 蔡存哲:OS還是得主動呼叫sbi去清除timer的樣子,不會因為trap進handler,硬體就自動清除pending imterrupt
我:我也不是很懂ececution environment指哪些东西,可能意思是交给M mode去做了,比如sbi。mip倒是能直接管理STIP
《RISCV体系结构编程与实践》p.162提到了通过mip+mideleg的方式将时钟中断委托给S mode,直接用mideleg不行吗?
f. sbi_call: remote fence
后面运行还会触发RemoteSFenceVMA_ASID,按照sbi手册内容,仿照之前的内容进行添加即可。
g. success

1 | |
6. 优化/完善
TODO 数据竞争风险?上锁? 中断注入?
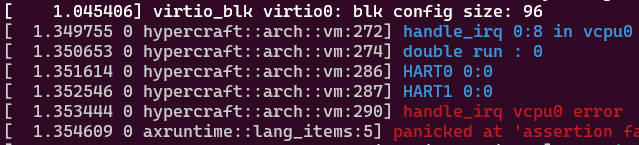
随机hart启动,启动hart不为0号的情况下,会出现模拟外部中断irq == 0?在debug_vm_pgtable后面,不知道有没有关系。
1 | |
所以plic这块是什么情况?
RISC-V入门(5)- 中断 - 如云泊 (fly0307.github.io)
为什么读取hart1的claim/complete寄存器能正常工作? 因为qemu-virt的虽然仿照了FU540,但在PLIC等部分有些许不同,比如FU540的context_0对应hart_0的M mode,context_1对应hart_1的M mode;而qemu-virt将context_0/1分配给了hart_0的M/S mode,因此在qemu-virt部分,hart的S mode对应的contex_id应该为
context_id = vcpu_id * 2 + 1;
改0x60_0000后爆炸
1 | |
1 | |
m mode软件中断爆炸?
1 | |
正常情况下,plic应该响应一个8号或10号中断。翻了好一会没找到这两对应的是啥,文档也没找到。最后到qemu仓库里翻到了相关的,和书上写的差不多能对上。
todo仓库代码链接
qemu-virt定义中,1-8号是virtio,其中8号是块设备(磁盘吗),10号是uart。不知道我找的对不对(害怕
https://github.com/qemu/qemu/blob/046a64b9801343e2e89eef10c7a48eec8d8c0d4f/include/hw/riscv/virt.h#L91
qemu -d 可以输出日志
https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2012/labguide.html https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2012/labguide.html#qemu--d
如sbi手册中所说,clear_ipi()可以被废弃,直接修改sip.ssip可以达到同样效果。
1 | |
但是项目中rust
riscv库的sip默认没有write(...)方法,只有read,有点怪。
库框架中提供了宏,可以很方便的自行添加write(...)。
1 | |
7. 进阶任务:多绑定
在一个物理核心上运行多个vcpu。这需要一个切换机制,可以简单选择时钟中断为切换信号。当收到时钟中断后,可以让vcpu/vm以一个特殊VMExit信息(???)退出,在hypervisormain/secondary_main中,通过perCpu的vcpu_queue获取其他绑定到此hart的vcpu,对其进行vm.run(...)。这要求vm.run(...)能够在退出前保存gprs,并在下次运行时恢复现场。
1 | |
这种情况下,中断要面临的问题更复杂一些。
假设目前只有一个物理cpu,上面要运行两个vcpu。vcpu0作为主核启动了guest
linux,在启动过程中,主核会向从核发送ipi,即向vcpu1发送ipi。然而,vcpu0/1都对应同一个物理核,我们不能像单绑定一样,直接对目标核心sbi::send_ipi,这等价于自己对自己发ipi。
因此hypervisor在捕获sbi::send_ipi行为后,要么立即切换vcpu1运行,要么将此行为缓存下来,等vcpu1运行时再发送?
理论上,所有涉及hart_id的sbi_call都需要进行类似的处理???
a. vs寄存器的保存/切换
本来在1:1的情况下,每个vcpu都独占vs csr;这在多绑定情况下失效了,vs csr需要被vcpu们共享。
因此,需要添加对vs csr的load/store。代码中给出了这部分寄存器,但没有使用到,按照框架照猫画虎添加就行了。
加完测试一下能不能跑动就行。
b. 复用时钟中断
host通过主动设置定时器来管理vcpu的切换。表现为进入vm.run(...)后,读取当前时间,并据此设置下一个定时器。
问题在于,guest本身也会设置timer,当时钟中断来临,我们需要判断这是对应谁设置的定时器。这可以通过比较当前时间是否超过目标时间来确定。
此外,sbi::set_timer(...)会覆盖上一个定时器,因此当处理完guest
timer后,若没有超出时间片,还需重新设置host的timer。
c. 延迟执行/注入?
如开头所述,由于vcpu不再独占hart,而sbi_call又是针对hart执行的,因此需要做特殊处理。
例如,当vcpu0执行send_ipi(hart_id: 1)时,并不能直接运行此函数,毕竟此时并没有hart1,而是应该将其缓存到一个类似于ipi_flag[vcpu_id] = true的结构中。当vcpu1开始运行时,检查ipi_flag[1]标志来确认进入vcpu1虚拟化模式前是否需要send_ipi(hart_id: 0)。
todo. 卡了
折腾过后发现能启动,但启得不是很动,能打印启动信息,显示成功bring up
cpu。能够完成Freeing unused kernel image (initmem) memory,但是无法运行init。并且有概率卡在debug_vm_pgtable: [debug_vm_pgtable ]。
查看过后疑似qemu卡在了wfi,很可能是对应了kernel中的cpu_do_idle()。不知道是为什么。
1 | |
1 | |
其次,根据vmexitinfo,可能是在kernel_init()-->mark_readonly()-->mark_rodata_ro()前出了问题,因为mark_rodata_ro()中会执行remotefence。在正常的启动记录里,是有这个的;然而当前却没有。
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
是哪没搞好捏,感觉烂尾了
99. doing: plic
观察到一个现象:qemu-virt plic的claim/complete寄存器会在读取后自动清0,不知道是不是qemu的实现而已,手册中没有见到相关内容:
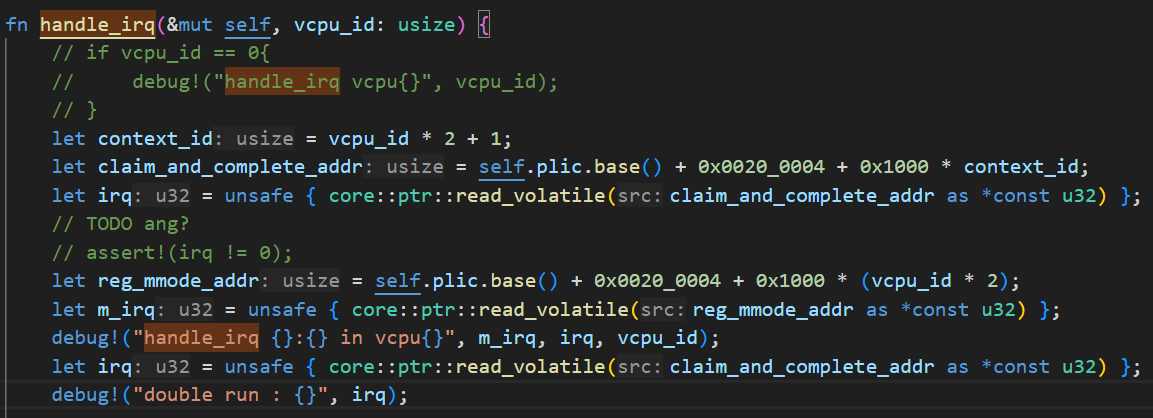
不过这确实算有问题吗?不管这个0一样可以正常运行。
plic手册也提到0就是没有待处理中断而已:
1 | |
别扭的地方只在于有了外部中断却不知道是谁发起的,无视这一点会对系统产生什么影响?
?. 后日谈
到做hypercraft重构的时期我才差不多完全明白了它的设计。
做了以下两步操作,才让vm_exit完全在vmm进行处理。
- 关闭sstatus.sie
- 进入虚拟机前替换stvec为_guest_exit
这样造成的效果是:当系统处于HS mode的vmm时,由于sstatus.sie是关闭的,因此它不会响应中断。当系统处于vm时,由于VS/VU mode特权级比HS mode低,因此sstatus.sie被视为永久开启,此时中断会被响应,并进入stvec = _guest_exit回到vmm中。
00. /bin
flowchart TB
subgraph axhal
h1[mod.rs::extern #quot;C#quot; rust_entry]
h2[mp.rs::fn start_secondary_cpu]
h3[boot.rs::extern #quot;C#quot; fn _start_secondary]
h4[mod.rs::extern #quot;C#quot; rust_entry_secondary]
end
h1-->r1
h2-->h3
h3-->h4
subgraph axruntime
r1[lib.rs::extern #quot;C#quot; rust_main]-->m1
m1[mp.rs::fn start_secondary_cpus]-->h2
end
flowchart TB
subgraph axhal
subgraph mod.rs
h1[extern #quot;C#quot; rust_entry]
h4[extern #quot;C#quot; rust_entry_secondary]
end
subgraph mp.rs
h2[start_secondary_cpu]
h5[rust_main_secondary]
end
subgraph boot.rs
h0[extern #quot;C#quot; _start]
h3[extern #quot;C#quot; _start_secondary]
end
he[wfi]
end
h0-->h1
h1-->r1
h2--"sbi::hart_start"-->h3
h3-->h4
h4-->h5
h5-->he
subgraph axruntime
subgraph lib.rs
r1[extern #quot;C#quot; rust_main]
end
subgraph mp_.rs
m1[start_secondary_cpus]
end
end
r1-->m1
m1-->h2

